Explain Why Methyl Cation Has a Different Three Dimensional
8 Explain why CH3 methyl cation has a different three dimensional geometry to CI-13- methyl anion. 8 Explain why CH3 methyl cation has a different three dimensional geometry to CH3-methyl anion.

The Geometry Of A Methyl Carbocation And Methyl Carbanion Class 11 Chemistry Cbse
Predict the approximate bond angles in a.

. The most abundant reaction product is the methyl cation CH 3. There are two reasons that combine to explain this angular deformation in ethene. Triphenyl methyl cation is very stable due to resonance.
The role of the methyl ion in the fragmentation of CH 4 2 New Journal of Physics 2009. The colors show the phase of the function. 3 Predict the two products you would isolate from the following reaction.
Causing the lowering of energy and making the carbocation very stable. Acids and Bases Polar and Nonpolar Molecules Organic Chemistry. For unlimited access to Homework Help a Homework subscription is required.
First lets talk about what is. Note however that the 2s orbital has 2 phases one of which is not visible because it is inside the other. Isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula.
It has three identical bonds each with a bond order of 1 13. Well this structure doesnt exist. 1 Using both words and pictures explain why ethyl cation is more stable lower in energy than methyl cation 2 Describe hyperconjugation in your own words.
The hydrogen atom has only one electron and so is a radical. The distribution is centered isotropically around the center of mass at far lower velocities compared to the product ions from the other two reaction pathways which are centered at the neutral beam velocity see Fig. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm.
Structure and Function 5th Edition - K. Ions which are formed by loss of an electron are termed as cation whereas ions which are formed by g. Here we present the three-dimensional structures of the covalent glycosyl-enzyme complexes formed by the T.
The H-C-H bond angle in ethene is ca. Analysis of the kinetic energy distribution reveals two. Vollhardt Neil Eric Schore All the textbook answers and step-by-step explanations.
117 degrees and the H-C-C angle is ca. For an organic compound rotation about a σ bond can produce different three-dimensional structures called conformational isomers or conformers. A short summary of this paper.
410 və-SEP-ər is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. For example by using solid and dashed wedge formula the 3-D image of a molecule from a two-dimensional picture can be perceivedIn these formulas the solid-wedge is used to indicate a bond projecting out of the plane of paper towards the observer. In triphenyl methyl carbocation positive charge can be deiocalized in all the 3 ring system.
Up to 256 cash back Explain why the methyl cation CH3 is less stable than the cation CH2Cl through. All electron groups are bonding pairs BP. In a Newman projection which represents the view along a CC axis the eclipsed conformation has the CH bonds on adjacent carbon atoms.
Hintone is trigonal planar and the other is tetrahedral. Solution for Which of the following explains why methyl anion has a pyramidal geometry while methyl cation is planar. We minimize repulsions by placing the three groups 120 apart Figure 632.
While the monopositive cation of helium is the only species of that element that has an odd number of electrons. 3pts Org 1 final Page 5. Answer 1 of 9.
The hydrogen cation has no electrons while the hydrogen anion and the helium atom each have a pair of electrons and so all of these species are not radicals. In chemistry a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a moleculeThis function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The methyl cation affinities of the rare gases have been calculated at 0 and 298 K by using coupled cluster theory including noniterative quasiperturbative triple excitations with the new.
9 Which of the above species is a better electrophile. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. The HOMO energy decreases upon.
With three bonding groups around the central atom the structure is designated as AX 3. Why this structure is stable. The figure below shows the first five solutions to the equation in a three dimensional space for a one electron atom.
Differences in three-dimensional structure resulting from rotation about a σ bond are called differences in conformation and each different arrangement is called a conformational isomer or conformerIsomers whose three-dimensional structures differ because of rotation about a σ bond. 37 Full PDFs related to this paper. In this diagram blue stands for negative and red stands for positive.
The three-dimensional 3-D structure of organic molecules can be represented on paper by using certain conventions. Important Points To Remember. Primary carbocations have a maximum of 3 σ-bonds capable of hyperconjugation secondary a maximum of 6 tertiary a maximum of 9 hence why the tertiary is the most stable cation out of the simply alkyl groups the allyl and benzyl systems in the diagram above are stabilised through delocalisation of the charge onto the pi system.
First from these bond angles and Coulsons Theorem ref_1 ref_2 we can determine that the C-H sigma bonds are s p X 22 hybridized and the C-C sigma bond is s p X 17 hybridized. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one. Further four H atoms also use these four sp 3 hybrid orbitals of carbon to form C-H sigma bonds which ultimately leads to the formation of the methane molecule.
Rangeli sialidase with two different mechanism-based inactivators at 19 and 17. Especially in India Many people have named this phenomenon of stability with a bizarre name like Dancing Resonance which is absurd. 12pts 9 Briefly explain which of the two above geometries best describes CH3 methyl radical.
Valence shell electron pair repulsion VSEPR theory ˈ v ɛ s p ər v ə ˈ s ɛ p ər VESP-ər. Catalytic H20 4 Calculate the degrees of unsaturation for compounds with the following molecular formulas. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S.
This is because one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals in the valence shell of carbon combine to form four sp 3 hybrid orbitals which are of equal energy and shape.
Methyl Salicylate C8h8o3 Pubchem

Ideal Gas Law In Terms Of Density

Learning Chemistry Carbon Compounds Short Note Posted Study Chemistry Chemistry Organic Chemistry

Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution With Arenediazonium Salts Organic Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Teaching Chemistry

What Is Methyl Cation Methyl Anion And Methyl Radical Organic Chemistry Digital Kemistry Youtube

Methanol Structure And Chemical Formula In 2021 Methylation Alcohol Chemical Formula
N Methylbenzylamine C8h11n Pubchem
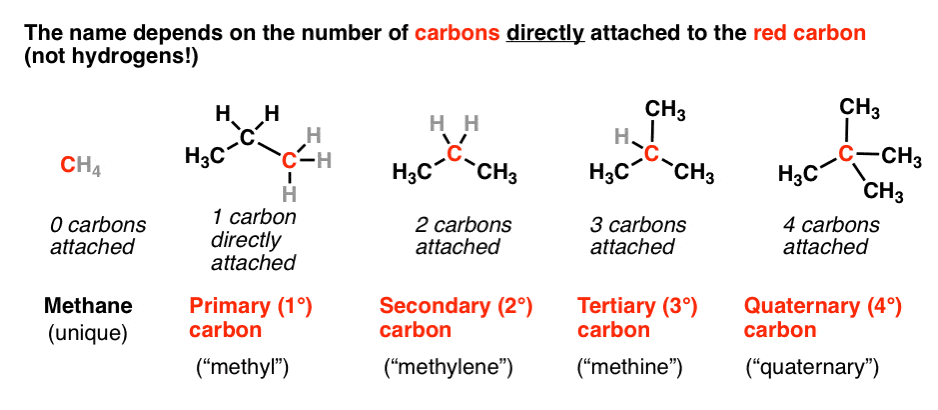
Primary Secondary Tertiary And Quaternary In Organic Chemistry

Elimination Reaction Definition Of Elimination Reaction The Reaction In Which Two Atoms Or Groups Or One Atom And One Group Methylation Reactions Molecules

Ch3 Methyl Anion Molecular Geometry Bond Angles Youtube

If Both Assertion And Reason Are True And Reason Is The True Explanation Of The Assertion
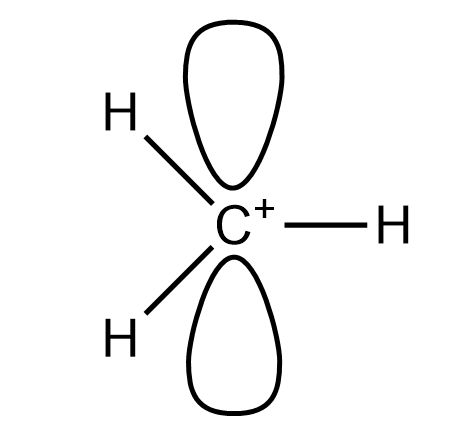
The Geometry Of A Methyl Carbocation And Methyl Carbanion Class 11 Chemistry Cbse

2 Methyl 2 Butanol C5h12o Pubchem

3 Methyl 2 Butanol An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Carbonyl Compound Organic Chemistry Books Organic Chemistry Physical Chemistry

Ak Lectures Methyl Cation Methyl Anion And Methyl Radical Intermediates

What Is Hyper Conjugation Or Baker Nathan Effect And Its Stability Chemsolve Net Organic Chemistry Books Teaching Chemistry Organic Chemistry

Shape Of Methyl Carbanion Is Chemistry Questions

Methyl Radical Definition Formula Formation Lewis Structure Shape Bond Angle And Hybridization Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment